SAMA cyber security framework compliance

According to Gartner, cybersecurity is one of the top risks facing Middle East and North Africa (MENA) businesses and financial institutions in 2019. As is the case around the world, banks are looking for innovative ways to combat cyber threats such as malware, phishing, and account takeover fraud – while also optimizing the customer experience and strengthening compliance.
I recently returned from the IDC Banking & Finance Congress in Riyadh, where cybersecurity and compliance with regulations such as the SAMA Cyber Security Framework were as much a part of the discussions as digital customer experience. The need to protect data, transactions, devices, and users through fraud prevention, mobile app security, and strong customer authentication is becoming deeply embedded in banks’ growth strategies. Throughout the Middle East, we are seeing a lot of focus on leveraging emerging technologies to innovate in this area, particularly as mobile banking gains ground in our region. To support this, InfoSec spending in MENA is expected to increase almost 10% over last year, rising to USD $1.9 billion in 2019.
SAMA cyber security framework compliance
To improve resilience against cyber threats, the Saudi Arabian Monetary Authority (SAMA) introduced of the SAMA Cyber Security Framework in May 2017. This follows a global trend where government and banking industry regulators around the world are introducing cybersecurity standards and guidance. A good example is the revised European Payment Services Directive (PSD2) with its Strong Customer Authentication requirements, which has since become a catalyst for secure Open Banking around the world, including in Bahrain.
The Saudi Arabian Monetary Authority developed the regulation based on industry standard frameworks such as the:
- National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) Framework for Improving Critical Infrastructure Cybersecurity (NIST CSF)
- Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS)
- ISO 27001/27002 Information Security Management Standards
- Information Security Forum Standard of Good Practice for Information Security
- Basel II International Convergence of Capital Measurement and Capital Standards (note: new adjustments were just endorsed on 14 January 2019 as part of Basel III)
It is mandatory for all banks, insurance companies, and finance companies operating in Saudi Arabia to adopt the SAMA Cyber Security Framework.
4 key focus areas for SAMA compliance
During my presentation at the conference, I explained the cybersecurity strategies and technologies that the Kingdom’s banks should adopt – not only for full compliance with SAMA, but also to build digital trust with their customers since this is the key to unlocking future growth.

Here are four key aspects of the Framework:
1. Identity & Access Management: In section 3.3, Cyber Security Operations and Technology, SAMA provides directives on Identity and Access Management (IAM). The Framework specifies multi-factor authentication (MFA) for privileged and remote access management. Banks require MFA for two purposes:
- To protect customers’ data and financial assets by using strong authentication to secure the customer’s login to online and mobile banking.
- To secure employees’ remote access to the corporate network and VPN, and protect against bad actors trying to access and steal data.
In addition to logins, the Framework also mandates MFA for these use cases:
- Adding or modifying beneficiaries
- Adding utility and government payment services
- High-risk transactions (when it exceeds pre-defined limits)
- Password reset
There are many multi-factor authentication options in the market. Saudi banks should look for a vendor that supports a wide range of authentication methods across different channels, including hardware tokens and software authentication for mobile users. The latest cloud-based multi-factor authentication solutions leverage step up authentication, also known as Intelligent Adaptive Authentication, enabled through mobile apps with native biometrics, FIDO U2F or UAF, behavioral biometrics, and more.
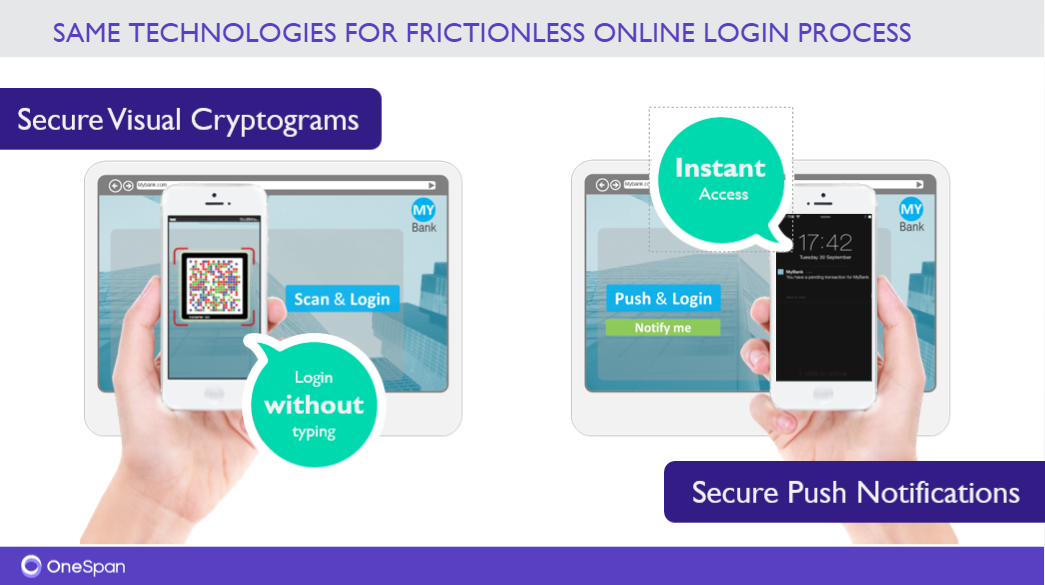
2. Secure Channel: In section 3.3.13, Electronic Banking Services, SAMA requires the “use of communication techniques to avoid man-in-the-middle attacks (applicable for online and mobile banking).” In this type of attack, fraudsters will position themselves between the bank and the customer in order to intercept the communication. Such an attack could change a genuine transfer of 5,000 SAR to a friend into a rogue transfer of 50,000 SAR to an imposter, without the customer being aware of it. One of the most common ways this happens is through a malicious Wi-Fi network or public hotspot (known as a rogue access point). Consumers enjoy the convenience of public hotspots, unaware that they may be transferring their payment data through a network controlled by a bad actor. To protect customers from man-in the-middle attacks, banks can implement Cronto® secure visual cryptograms. To see this in action, read this blog or watch a video.
3. Mobile Application Shielding: In section 3.3.13, Electronic Banking Services, SAMA outlines requirements for mobile app security. This covers requirements such as preventing and detecting attempts to alter mobile app code, sandboxing techniques, and mitigating the various risks of the mobile app being compromised. One of the important considerations when it comes to mobile is the fact that users are not sufficiently aware of the threat landscape and do not always take the necessary protection measures – especially on Android. According to GlobalStats, Android leads the mobile market in the Kingdom at 65% to 34% for iOS.
At the same time, many banks have not yet developed mobile applications, don’t monitor the mobile channel, or don’t have enough experience with mobile fraud. Yet mobile malware is increasing. According to Kaspersky Lab, the number of banking Trojans attacking users of mobile devices doubled in 2018. That is why applying proactive, client-side security measures such as mobile app shielding has become a necessity. With the right security measures and MFA mechanisms in place, banks and other financial institutions can not only defend the app against attacks, but also simplify the user experience. It is critical that banks provide the most convenient authentication methods, including mobile biometrics, and keep advanced mobile app security running in the background, invisible to the user.
4. Fraud Detection and Prevention: In section 3.3.16, Threat Management, the Framework specifies the use of fraud and risk management. As more financial products are offered via digital channels, a bank’s attack surface grows exponentially. To keep pace, the global market is turning to machine learning and sophisticated data mining and modeling to gain the most accurate predictions of risk and fraud. Modern fraud detection and prevention platforms analyze vast quantities of data from multiple sources across all digital channels to ensure the most accurate risk score. These scores drive intelligent workflows that enable immediate action based on pre-defined and/or bank-defined security policies and rules.
According to Forrester’s Fraud Management Solutions Forecast, 2017 To 2023 (Global), global spending on fraud management solutions is expected to double over a five year period. The key to extracting full ROI from fraud management spending is to work with a vendor who will make you successful in achieving the twin goals of strong security and an optimal user experience.
For today’s digital banking customer, transacting with their financial provider has to be as easy as it is secure. It should be so easy and frictionless that customers don’t even think about the security. Security has to be done well to create the best possible customer experience, since this will drive growth through improved customer loyalty, retention, and use of digital and mobile banking services.