Content from Infographic
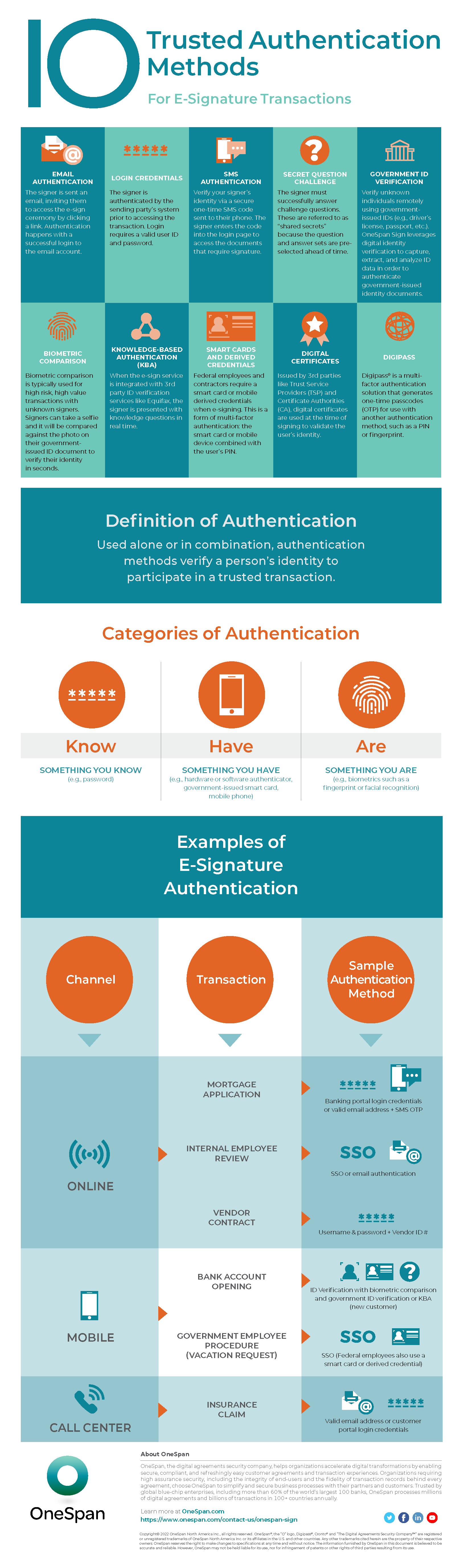
10 Trusted Authentication Methods for E-Signature Transactions
Use these authentication methods for e-signature alone or in combination (single or multi-factor authentication), depending on the risk level of your process:
- Email authentication: The signer is sent an email, inviting them to access the e-sign ceremony by clicking a link. Authentication happens with a successful login to the email account.
- Login credentials: The signer is authenticated by the sending party’s system prior to accessing the transaction. Login requires a valid user ID and password.
- SMS authentication: Verify your signer’s identity via a secure one-time SMS code sent to their phone. The signer enters the code into the login page to access the documents that require signature.
- Secret question challenge: The signer must successfully answer challenge questions. These are referred to as “shared secrets” because the question and answer sets are pre-selected ahead of time.
- Government ID verification: Verify unknown individuals remotely using government-issued IDs (e.g., driver’s license, passport, etc.). OneSpan Sign leverages digital identity verification to capture, extract, and analyze ID data in order to authenticate government-issued identity documents.
- Biometric comparison: Biometric comparison is typically used for high risk, high value transactions with unknown signers. Signers can take a selfie and it will be compared against the photo on their government-issued ID document to verify their identity in seconds.
- Knowledge-based-authentication (KBA): When the e-sign service is integrated with 3rd party ID verification services like Equifax, the signer is presented with knowledge questions in real time.
- Smart cards and derived credentials: Federal employees and contractors require a smart card or mobile derived credentials when e-signing. This is a form of multi-factor authentication: the smart card or mobile device combined with the user’s PIN.
- Digital certificates: Issued by 3rd parties like Trust Service Providers (TSP) and Certificate Authorities (CA), digital certificates are used at the time of signing to validate the user’s identity.
- DIGIPASS: DIGIPASS® is a multi-factor authentication solution that generates one-time passcodes (OTP) for use with another authentication method, such as a PIN or fingerprint.