eSignature authentication methods: Strike the right balance with secure, user-friendly authentication

Businesses are evolving to stay competitive in an increasingly digital world where customers expect a convenient, secure, and seamless experience. As a result, more companies are implementing electronic signatures with digital signature technology as part of their digital transformation strategy.
Not only are eSignatures legal, but they provide multiple benefits to users. However, organizations still need to focus on security since they must know who they are doing business with, in their online and mobile channels.
As an organization, it's important to strike the right balance between customer experience and security when implementing user authentication. This will increase completion rates and minimize customer abandonment from cumbersome authentication. Depending on your use case and authentication needs, the best approach is to look for eSignature software that supports a wide array of authentication methods. This ensures the best user experience while mitigating risks of fraud.
Additionally, you want to ensure that the authentication options will meet the requirements of your eSignature processes and channels. For example, an electronic signing process that occurs face-to-face in a bank branch or with an insurance agent will often use different authentication methods than a remote transaction through a website.
Identification vs. authentication
The terms “user identification” and “user authentication” may sound similar, but they have different meanings.
User identification is the process of presenting and making a claim to an identity. This is the first step in determining who you're doing business with. Naturally, it takes place the first time two parties conduct a transaction.
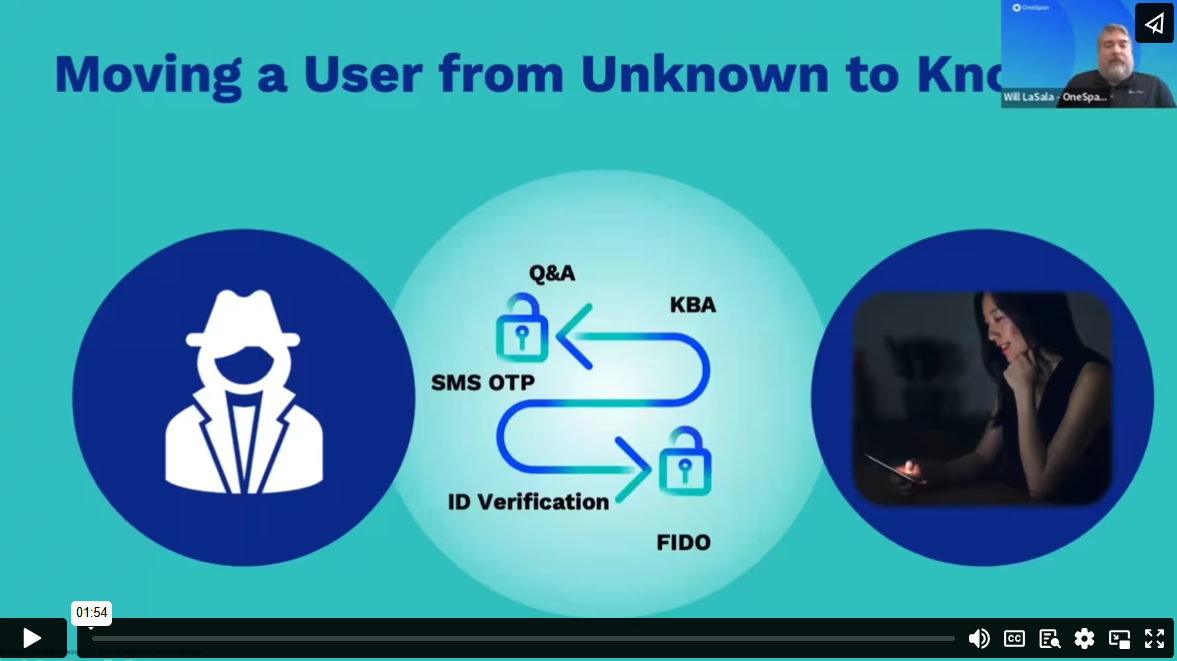
A good example is a new applicant who goes to the bank to open an account for the first time. The bank asks the applicant to prove their identity using their driver’s license, passport, or national ID card. To verify a new applicant’s identity remotely through your digital channels requires digital identity verification. The digital identity verification feature in an electronic signature solution makes it possible to quickly and securely confirm that an “unknown user” is who they say they are – directly through their mobile device.
Once the individual’s identity is confirmed, they become a customer or “known user”. They receive credentials for future transactions.
User authentication is the process of verifying those credentials prior to giving access to a system. In this case, we're referring to the act of eSigning. This alternative offers better security and a better user experience than a handwritten signature.
eSignature authentication methods
OneSpan Sign offers a number of authentication methods to be sure that only the correct signers access your eSignature transactions. Whether used alone or in combination, these authentication methods verify a person’s identity and create a trusted transaction.
Email authentication
Signers receive an email with an embedded link inviting them to sign. Accessing the email and clicking the link authenticates the signer. This authentication method establishes a connection to the signer because of the uniqueness of their email address and the fact that they are logged in to their email account.
Login credentials (including single sign-on or SSO)
Signers can access documents upon logging in to an online portal with a valid user ID and password. In the online banking portal example, the customer logs in to their account and can eSign the documents from the portal.
One-time passcode sent by text message
A unique PIN is automatically generated and sent to the signer’s phone by SMS. The signer enters it into a login page, then gains access to the documents that require signature.
Secret question challenge (static KBA or Q&A)
A signer has to answer challenge questions to authenticate before they can view the electronic documents. Both the signer and the sender determine these questions and answers ahead of time for the authentication to work.
Dynamic KBA
OneSpan Sign can integrate with third-party ID verification services like Equifax. In this case, the sender asks the signer personal questions. These questions are created on the spot to confirm their identity before signing. Generated in real-time, these questions make it difficult for anyone other than the actual user to answer correctly.
Digital certificates
OneSpan Sign leverages digital certificates issued by third-party Trust Service Providers (TSP) and certificate authorities (CA). When eSigning using a personal digital certificate, signers must use both the certificate and their PIN or password to authenticate. When using a digital certificate issued by a qualified trust service provider, this creates a qualified electronic signature (QES) per the requirements of the European Union’s eIDAS regulation.
Smart cards & derived credentials
Government employees and contractors require a smart card or mobile-derived credentials when eSigning. Smart cards like Common Access Cards (CAC) and Personal Identity Verification (PIV) cards store digital certificates. This form of multi-factor authentication consists of something the user knows (the PIN for their smart card), something the user has (the smart card), and sometimes a biometric identifier (something the user is).
ID verification
You can verify unknown individuals remotely using government-issued IDs (e.g., driver’s license, passport, etc.). OneSpan Sign leverages digital identity verification to capture, extract, and analyze ID data to authenticate government-issued identity documents.
Digipass®
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) provides added security by requiring two or more verification methods. OneSpan Sign integrates with OneSpan’s MFA solutions like Digipass to support strong authentication with one-time passwords (OTP) and/or visual cryptograms.
Biometrics
Biometrics are typically used for high-risk, high-value transactions with existing customers. Signers can use their mobile device to take a selfie, which will be compared against their government-issued ID document. During active liveness detection, the system presents the user with specific challenges or tasks that require a live response such as blinking, speaking, or head tilting. This ensures the photo captured is from a real human. Passive liveness detection works invisibly in the background without interrupting the user experience, analyzing additional biometric elements provided during the authentication process. Signers can be verified in real-time, in seconds.
FIDO passkeys
- This innovative method enables a smooth and easy authentication process by creating a secure channel between sender and signer. In turn, this increases sign-in success rates and reduces operational costs. Passkeys offer near-instant authentication directly on the user’s device by leveraging device biometrics. They can also work offline after initial setup, removing dependency on network availability. Passkeys are supported across a wide range of platforms, browsers, and devices and provide cross-device sync. They're well suited to repeat signers.
Hear the full presentation: Accelerate Banking Transformation with OneSpan
OneSpan Sign electronic signature software provides the flexibility to support your authentication requirements for a variety of signing scenarios. Read our User Identification and Authentication white paper for best practices on how to select the right authentication methods for your eSignature use case.